For any business with international operations, currency fluctuations can quietly erode profits, strain budgets, and make cash flow forecasting a nightmare. If your business deals with suppliers, clients, or subsidiaries in multiple currencies, you’ve likely felt the sting of FX volatility.
Yet, many businesses either ignore currency hedging or see it as something which is reserved for massive corporations with in-house treasury teams. That couldn’t be further from the truth. Whether you’re a scaling e-commerce brand or a 300-person logistics firm, having a strategic approach to currency management is essential.
This guide will help you move beyond the basics, providing a practical decision-making framework so you can assess if, when, and how to hedge your FX exposure.
What is currency hedging (and why should you care?)
Let’s start with the fundamentals. Currency hedging is often misunderstood, but it’s a vital part of international financial management. We aren’t talking about speculation or trying to predict the future; it’s about protecting your business from unwanted surprises.
Currency hedging is the act of reducing risk caused by foreign exchange rate movements. This can be done by locking in an exchange rate or using financial instruments to protect against adverse currency moves.
Why it matters
Even a relatively small percentage exchange rate swing can have a significant impact on your profit margins. For example, if you’re paying a supplier €100,000 and the GBP/EUR rate moves from 1.15 to 1.13, that’s a £1,500 difference.
Recent market data illustrates this point clearly.
Over the last 12 months, GBP/USD moved between 1.22 and 1.37, while CHF/JPY saw volatility (166 to 185) driven by central bank policy changes and rate divergence. A business making regular payments during those windows without a hedging strategy could face serious and unexpected cost increases.
Businesses hedge to:
- Protect margins
- Improve forecasting
- Safeguard against market shocks
- Build financial resilience
These benefits go well beyond currency protection – they contribute to broader business stability and long-term planning confidence.
Common misconception: Hedging isn’t about speculation. It’s about managing known exposures and gaining predictability.
Business scenarios where hedging is essential
Theory is always helpful, but let’s look at some real-world business scenarios and context. Firstly, not every organisation will need a complex hedging strategy, but there are key operational signs that suggest hedging could add value.
It’s always important to note that hedging is not a one-size-fits-all solution. To put this in practical terms, here are common scenarios that might call for a currency hedging strategy:
1. High FX exposure
Businesses exposed to volatile currencies or with regular foreign currency payments and receipts are most vulnerable to FX risk.
- You operate in countries with volatile currencies
- You invoice or receive payments in foreign currencies
2. Long-term contracts
If your business has contractual obligations in foreign currencies, market movements could impact profitability unless rates are fixed in advance.
- You have fixed-price agreements with overseas partners
- Any delay between invoicing and payment exposes you to currency swings
3. Large capital commitments
Major investments abroad create large exposures over extended time periods.
- Real estate, M&A, or equipment purchases abroad
- A 3% currency swing on a seven-figure transaction could be material
4. Seasonal or predictable cash flows
Regular payments in foreign currencies offer ideal conditions for structured hedging.
- Consistent monthly payments abroad (e.g., payroll, vendor costs)
- Easier to hedge when timing and amounts are known
The ability to recognise these triggers early allows you to take a proactive approach, avoiding surprises that could affect your margins.
The currency hedging decision matrix
Let’s move the process ahead and get tactical.
Once you’ve identified your FX exposure, the next step is figuring out the right level of hedging. To help you, we’ve developed a simple framework using three variables to help guide your decision:
- Exposure level: Low, Medium, High
- Time horizon: Short, Medium, Long
- Cash flow predictability: Low, Medium, High
This matrix helps you match your FX reality with appropriate tools and strategies.
Decision Matrix:
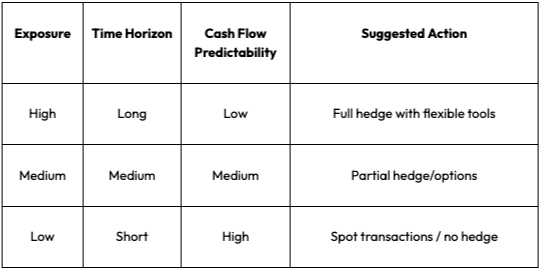
You can see the table, but it would be helpful to break that down and look at some everyday use cases.
Scenario 1: High exposure, long horizon, unpredictable flows
- Example: You’ve secured a year-long contract to pay overseas manufacturers, but your order volumes vary month-to-month.
- Action: Use layered forward contracts or options to hedge a base amount while maintaining flexibility.
Scenario 2: Medium exposure, medium horizon, predictable flows
- Example: You pay €50,000 monthly to a European vendor for the next 6 months.
- Action: Consider a rolling 6-month forward hedge to lock in a blended rate.
Scenario 3: Low exposure, short horizon, predictable flows
- Example: Occasional overseas invoices or one-off purchases.
- Action: Use spot transactions and monitor rates, but formal hedging isn’t necessary.
This matrix gives you clarity on what action to take based on your operational context.
No two scenarios are the same
While this framework offers helpful guidance, it’s worth acknowledging that some businesses choose not to hedge. Often, this reflects a conscious strategic choice – whether due to minimal exposure, internal policy constraints, or a desire to maintain operational simplicity.
For example, businesses with short transaction cycles or natural currency offsets may decide that the administrative effort of hedging outweighs the benefit.
On the flipside, some finance teams even assign FX exposure a risk weighting – similar to credit or counterparty risk – as part of a broader treasury risk assessment before formalising their currency policy.
Hedging tools and tactics explained
Once you’ve identified your needs, it’s essential to understand the tools at your disposal. Think of them as instruments in your treasury toolkit. Used correctly, they offer protection, flexibility, and peace of mind.
Each business has unique requirements, but here are the most common currency hedging tools:
Forward contracts
- Lock in an exchange rate for a future date
- Best for companies with predictable cash flows
Options contracts
- Gives the right, but not the obligation, to exchange at a specific rate
- Suitable for volatile markets where flexibility is key
Natural hedges
- Match revenue and costs in the same currency
- Example: Pay EU suppliers in EUR if most of your sales are in EUR
Layered hedging
- Stagger hedges over time to smooth out rate fluctuations
- Ideal when you have regular recurring payments
Hybrid strategies
- Mix of spot, forward and options, depending on business needs
Knowing which tools to use and when can dramatically enhance the effectiveness of your overall strategy.
For finance teams operating under formal reporting standards, it’s also worth noting that accounting rules such as IFRS 9 (or local equivalents) may influence how hedging activities are reported in your financial statements. While a deep dive isn’t necessary at this stage, your FX consultant or finance controller should be aware of these implications when implementing forward contracts or options.
Triggers that signal it’s time to review your FX strategy
Your business isn’t static, and neither is the market. Currency conditions, competitive landscapes, and global economics evolve constantly.
Here are some indicators that it may be time to reassess:
- Expansion into new international markets
- Change in contract terms or volumes
- Material FX losses or surprises in your financials
- Significant macroeconomic or political events
- Annual budgeting or planning cycle
Monitoring these triggers helps ensure your strategy remains proactive rather than reactive.
While focusing on your business needs is critical, macroeconomic shifts also play a key role. For example, interest rate divergence between the UK and the US, or liquidity tightening by central banks, can fuel sudden currency swings. Keeping an eye on central bank policy, inflation reports, and geopolitical risks isn’t just for economists – these factors can directly affect your exposure and the timing of strategic decisions.
How to get started with a currency hedging strategy
If the idea of hedging still feels complex, don’t worry. Like any solid business strategy, it starts with understanding where you are today.
Here’s a 5-step path to building a tailored strategy:
- Audit your FX exposure
- Review suppliers, customers, loans, or investments in foreign currency
- Segment cash flows
- Group predictable vs unpredictable payments
- Define objectives
- Margin protection? Budget certainty? Flexibility?
- Choose your tools
- Based on the matrix and your business profile
- Review quarterly
- Adjust as your business and the market evolve
A strategic foundation like this helps future-proof your operations.
Why work with a currency consultant?
Partnering with an expert takes the complexity out of FX and adds a layer of insight that even the best spreadsheets can’t deliver.
A specialist FX provider like BLK.FX offers:
- Market analysis and rate tracking
- Bespoke hedging frameworks based on business-specific cash flows
- Access to better-than-bank rates and transparent pricing
- Ongoing advice to keep your strategy aligned
Whether you’re just starting or want to level up your current approach, expert guidance can save time and money – and also help you sleep better at night.
If we look at FX management in more detail, beyond protection, hedging can also become a pricing advantage. Businesses that stabilise their FX costs will be better positioned to offer fixed or predictable pricing to their clients. A commercial edge that can improve competitiveness, especially in high-volume or contract-based sectors.
Conclusion: Turn currency risk into a strategic advantage
Currency risk is inevitable, but unmanaged risk is optional. However, with the right framework, businesses of any size can approach hedging with confidence.
This isn’t about trying to beat the market. It’s about protecting what you’ve worked hard to earn. Start by assessing your exposure, use the matrix as a guide, and don’t hesitate to speak with a BLK.FX advisor who can help you make the right calls at the right time.
Ready to consider a different approach to your FX exposure?
Check out blkfx.co.uk and see what modern FX management looks like.